If your heart sometimes races, flutters, or skips a beat, you’re not alone. Millions of people experience arrhythmias—irregular heartbeats that can be harmless, annoying, or even dangerous. When medications don’t help or side effects become a problem, there’s a powerful, minimally invasive treatment that can offer lasting relief: Radiofrequency Ablation.
Let’s dive into what RFA is, how it works, and why more people are choosing it to reclaim their heart health.
💓 What Are Arrhythmias?
An arrhythmia is a problem with the electrical signals that control your heartbeat. It can cause the heart to beat:
-
Too fast (tachycardia)
-
Too slow (bradycardia)
-
Irregularly (atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, PVCs, etc.)
While some arrhythmias are mild, others can lead to fatigue, fainting, shortness of breath—or increase the risk of stroke and heart failure.
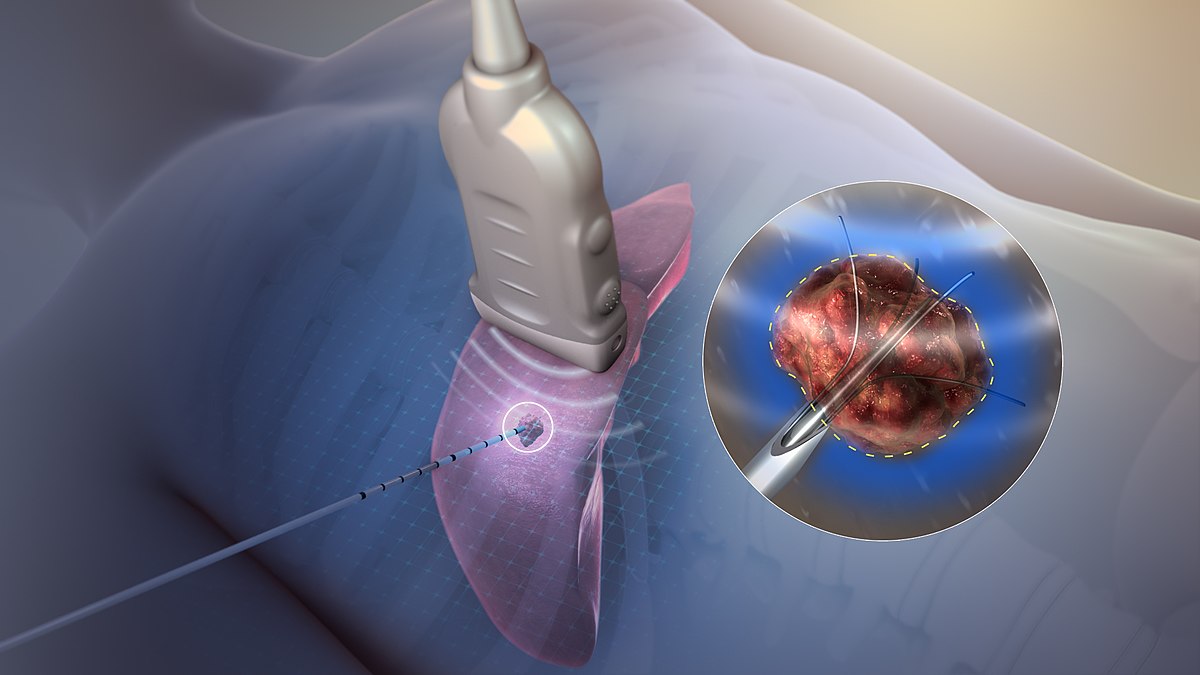
⚡ What Is Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)?
Radiofrequency ablation is a procedure that uses heat energy to destroy the tiny area of heart tissue that’s causing the abnormal electrical signals. It’s done by a cardiac electrophysiologist (a specialist in the heart’s electrical system).
In simple terms: If your heart’s electrical system is sending mixed signals, RFA is like hitting the “reset” button on the faulty circuit.
🏥 How the Procedure Works
RFA is performed in a specialized lab called an electrophysiology (EP) lab.
Here’s what to expect:
-
Preparation: You’ll get mild sedation or anesthesia. Electrodes will be placed on your chest to monitor your heart.
-
Catheter insertion: Thin, flexible wires (catheters) are inserted through a vein (usually in your groin or neck) and guided to your heart.
-
Mapping: The doctor uses advanced mapping tools to locate the source of the abnormal rhythm.
-
Ablation: Radiofrequency energy is delivered through the catheter to carefully destroy the problem tissue—without harming the rest of the heart.
-
Observation: The team monitors your heart to make sure the arrhythmia doesn’t return.
⏱️ Most procedures last 2–4 hours. You may stay overnight for observation or go home the same day.
🌟 Benefits of RFA
-
Highly effective, especially for conditions like:
-
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
-
Atrial flutter
-
Certain types of atrial fibrillation
-
Ventricular tachycardia (in select cases)
-
-
Minimally invasive
-
Reduces or eliminates need for long-term medications
-
Quick recovery time
-
Improved quality of life and heart function
🔄 Recovery and Aftercare
Most people return to normal activities within a few days. You might feel a little sore at the catheter insertion site, but serious complications are rare.
Your doctor may ask you to:
-
Avoid strenuous activity for a week
-
Monitor for symptoms like chest pain, fever, or bleeding at the catheter site
-
Follow up with heart rhythm monitoring to ensure success
🧠 Is RFA Right for You?
Not all arrhythmias need ablation—but if your symptoms persist despite medications, or you prefer a drug-free solution, RFA could be an excellent option.
Talk to your cardiologist or electrophysiologist if you:
-
Have symptomatic arrhythmias
-
Can’t tolerate heart rhythm medications
-
Want a long-term fix for a recurring heart rhythm problem
❤️ Final Thoughts
Radiofrequency ablation is one of the most effective tools modern cardiology has to offer. It’s safe, precise, and can be life-changing for people struggling with irregular heart rhythms.
If you’re tired of the flutter, racing, or skipping—ask your doctor if it’s time to take the heat to your arrhythmia.